Snow is water that falls from the clouds that had been frozen into a solid and like rain. Snow consists of water vapor particles are cooled in the air above, and then fall to earth as a piece of soft, white, and like crystal.
At a certain temperature (called freezing point, 0 ° Celsius, 32 ° Fahrenheit), normal snow melt and disappear. Process as snow / ice changes directly into water vapor without melting first called sublimes. Opponent process called deposition. The following are the basic forms of snow:
 |
| 1. Prism |
Prism shape is very thin so it is difficult to see by eye. looks like a wooden pencil.
 |
| 2. Stellar Plates |
Resembling a plate with six broad arms resemble stars. Usually decorated with symmetrical markings. Formed when the temperature is near -2 C (28 F) or near -15 C (5F) snow crystal morphology diagram.
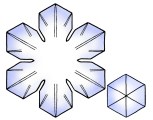 |
| 3. Sectored Plates |
Typical mountain that leads to the angles between adjacent facet prism. sides divided into six equal parts.
 |
| 4. Stellar Dendrites |
Dendrite means
"like a tree", so stellar dendrite snow crystal is a plate that has branches. The size is quite large, with a diameter of 2-4 mm. These crystals are easily seen with the naked eye.
 |
| 5. Fernlike Stellar Dendrites |
The shape resembles a fern. snow crystal is the largest snow crystals with a size of 5 mm or more.
 |
| 6. Hollow Columns |
Cone-shaped tube with a hole in it. is small and thus require a magnifying glass to see it.
 |
| 7. Needles |
Ice crystals formed at a temperature of 5 C (23 F). If we see with the naked eye, it resembles a small gray hair.
~source~








0 comments:
Post a Comment